Current Trends In Blockchain Application Development

Blockchain technology is essentially a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner, making it ideal for creating applications that require trust and security. Decentralized applications inherit the benefits of blockchain applications such as immutability, transparency, and security. Blockchain technology has seen significant growth and adoption in recent years and there are several current trends in blockchain application development that are shaping the future of the industry. Now, blockchain applications are being developed across various industry sectors and everyday new use cases are coming up. In this article, we discuss what we should know about blockchain application development as well as popular industry use cases of blockchain applications,
Before getting into details of blockchain applications development, developers need to have a solid understanding of underlying technology, such as consensus mechanisms, smart contracts, cryptography etc. First, we should identify the problem that we are trying to solve using blockchain technology and understand how it will add value over the traditional solution. Choosing the right platform for blockchain application development is very critical, as it will determine the development cost and scalability of the application in the future. There are some important factors that should be considered before choosing a blockchain platform for DApp development.
EVM Compatibility
Developing smart contracts using solidity language makes it compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). EVM compatibility refers to the ability of a blockchain to execute smart contracts written in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) bytecode. Smart contracts developed in solidity get executed on EVM, all transaction processes, data storage, calculation of gas, and operations of DApp in the Ethereum network get executed on it. Solidity is the most trusted and used language by smart contract developers and DApp developed in this language is compatible with Ethereum or any other EVM-compatible blockchain platform. There are more than 100 EVM-compatible blockchain platforms, the most used platforms are Ethereum, Tron, BCS, Arbitrum, Polygon, Optimism, Avalanche, Fantom, Cronos, Klaytn etc.
Security and Scalability
Security and scalability are important factors to consider when evaluating any blockchain, including EVM-compatible blockchains. EVM-compatible blockchains are generally considered to be secure due to their consensus mechanism and smart contract architecture. The consensus mechanism ensures that transactions are validated and confirmed by a distributed network of nodes, while the smart contract architecture allows for the execution of code in a secure and transparent manner. One of the main challenges facing EVM-compatible blockchains is scalability, or the ability to process a large number of transactions quickly and efficiently. The current architecture of EVM-compatible blockchains, which requires all nodes to validate and process every transaction, limits their scalability. To address this issue, developers are working on various scaling solutions, such as sharding, layer 2 scaling solutions like rollups, and sidechains. These solutions aim to increase the throughput of the blockchain without compromising on security.
Scalability is another key consideration for EVM-compatible blockchains, as high transaction volumes can put a strain on network resources and lead to slow confirmation times. To address scalability challenges, EVM-compatible blockchains can adopt various scaling solutions, such as sharding, state channels, or layer-two protocols.
Cross-chain interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability is the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and interact with each other, allowing users to transfer assets and data across different blockchains seamlessly. One of the most popular approaches to achieving cross-chain interoperability is through the use of "bridges," which are smart contracts or other software solutions that act as intermediaries between different blockchain networks.
EVM-compatible blockchains, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon, use the same EVM, which allows for greater compatibility and ease of communication between these networks.
One of the most popular solutions for cross-chain interoperability among EVM-compatible blockchains is the use of the Ethereum Bridge, also known as the ETH Bridge. The ETH Bridge is a two-way bridge that allows users to transfer assets between Ethereum and other EVM-compatible blockchains, such as Binance Smart Chain and Polygon. The bridge works by locking assets on one blockchain and minting a corresponding amount of wrapped assets on the other blockchain, allowing for seamless cross-chain transfers.
Another popular solution for cross-chain interoperability among EVM-compatible blockchains is the use of interoperability protocols such as Polkadot, which uses a relay chain to connect different blockchains in its ecosystem, including EVM-compatible blockchains.
Real-world data oracles
An oracle is a third-party service that provides data to a blockchain network. Oracles are essential for blockchain applications that require off-chain data such as real-world events, market data, and weather conditions. In the context of EVM-compatible blockchains, there are several real-world data oracles available. Here are some of the most popular ones:
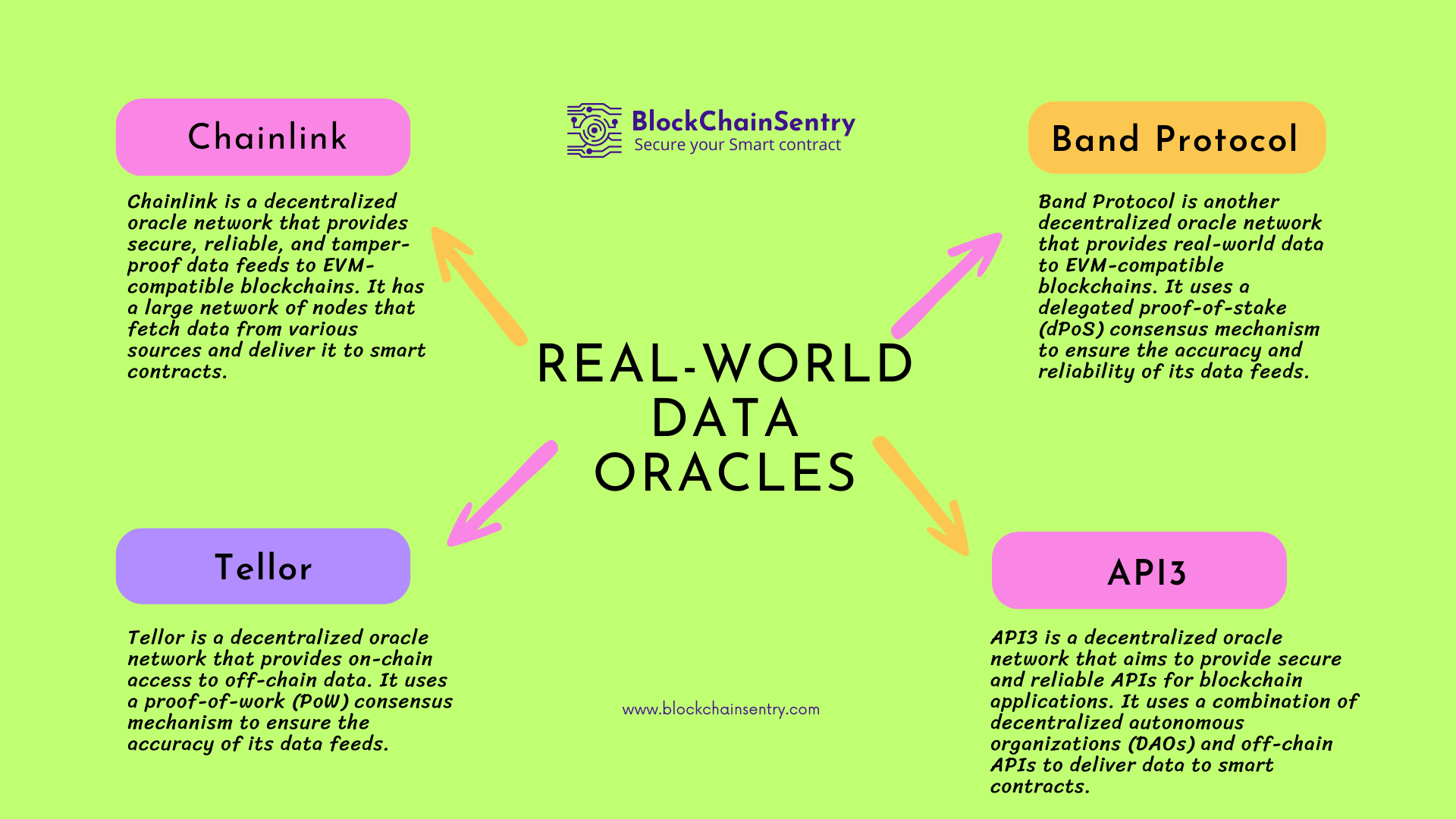
These are just a few examples of real-world data oracles for EVM-compatible blockchains. There are many other oracle networks and solutions available, each with its unique features and capabilities. When choosing an oracle, it's essential to consider factors such as security, reliability, decentralization, and the type of data that you need to access.
Community and Grants
Lastly, community and grants are also an important aspects of any blockchain project, including EVM compatible blockchains. Community refers to the group of individuals or organizations that are involved in and support a particular blockchain project. This can include developers, investors, users, and other stakeholders who contribute to the project's growth and success. A strong and active community is essential for the long-term success of a blockchain project, as it helps to drive adoption, encourage development, and provide feedback and support.
Grants are a way for blockchain projects to provide funding to developers and other contributors who are working on the project. Grants can be used to support the development of new features, improve performance, enhance security, and more. By providing grants, blockchain projects can attract and retain talented developers and other contributors, which can help to drive innovation and growth.
Popular Industry Use cases of Blockchain Applications
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
DeFi refers to a new financial system built on blockchain technology, enabling decentralized and trustless financial applications. This includes decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and stablecoins. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) on EVM-compatible blockchains refers to the ecosystem of financial applications built on Ethereum and other blockchains that support Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility. DeFi on EVM-compatible blockchains includes a wide range of financial applications, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending and borrowing platforms, derivatives markets, and more.
One of the primary benefits of building DeFi on EVM-compatible blockchains is the ability to leverage the existing Ethereum ecosystem, including the large developer community and rich tooling, such as the widely-used solidity programming language.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
NFT stands for non-fungible token, which is a type of digital asset that represents ownership of a unique item or piece of content. NFTs are unique digital assets that can be used to represent ownership of a wide range of assets, from digital art to collectibles and real-world assets. EVM-compatible blockchains, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon, have become popular platforms for creating and trading NFTs.
On these blockchains, NFTs are typically created using smart contracts, which are self-executing programs that run on the blockchain. These contracts define the rules for creating, owning, and trading NFTs, including their metadata (such as name, description, and image) and any additional functionality (such as royalties or unlockable content).
Supply chain management
Blockchain technology is being used to improve the transparency and efficiency of supply chain processes, such as tracking goods and managing inventory. Supply chain management on EVM-compatible blockchains involves using smart contracts to track and manage the flow of goods and services throughout the supply chain. This can include recording the origin, location, and destination of products, as well as their quality and other relevant information.
The benefits of using blockchain technology for supply chain management are, increased transparency, improved traceability, and reduced costs and risks.
Identity management
Blockchain technology can be used to build secure and decentralized identity systems, allowing users to control their own personal data and identity information. Identity management on blockchains is a process of verifying and managing digital identities of users who participate in blockchain-based systems. On a blockchain, identity management can be decentralized, allowing users to maintain control over their digital identities and personal information. There are several approaches to identity management on blockchains, including:
Public-key cryptography: This approach involves the use of digital signatures and public-key cryptography to verify the identity of users. Each user has a unique private key that they use to sign transactions, and a public key that other users can use to verify their identity.
Decentralized identifiers (DIDs): DIDs are unique identifiers that are stored on a blockchain and can be used to verify a user's identity. DIDs can be used to link different types of identity information, such as personal data, social media profiles, and government-issued IDs.
Self-sovereign identity (SSI): SSI is a decentralized approach to identity management that gives users complete control over their personal data. Users create their own DIDs and store their identity information on a blockchain, giving them full control over who can access their data.
Federated identity: This model involves the use of multiple blockchain networks or platforms to manage identity information. Each network or platform maintains its own identity information, but users can authenticate themselves across multiple networks using a shared identity.
Identity verification: Blockchain can also be used to verify the identity of individuals or organizations. This involves the use of smart contracts to validate identity information, such as government-issued IDs or biometric data.
There are several possible use cases of blockchain application development across sectors, which we are going to discuss in detail in our next blog posts. As a blockchain development and security firm BlockChainSentry is a market leader in providing web3 based blockchain application and security solutions to the customers as per the business flow requirements, write to us on hello@blockchainsentry.com for enquires.