What Is A Flash Loan Attack In DeFi

Unlike in traditional loans, where the applicant shares his identity proof, proof of income, and any other required documents, all these things are unnecessary in the world of blockchain. Raising a flash loan is quick and easy, as these loans are uncollateralized and granted immediately, allowing users to access the funds. In the crypto space, this is considered to be very useful for faster transactions and recorded quickly in a smart contract that is transparent and immutable.
The downside of this opportunity is if the vulnerabilities of a flash loan smart contract are not properly managed, then these become targets of cyber crimes. A flash loan attack is an exploit that takes advantage of a smart contract code flaw or its vulnerabilities. In a flash loan attack, the attacker borrows assets from a lending platform using a smart contract and then uses those assets to manipulate the market or attack another smart contract.
Flash loan attacks have significantly impacted the crypto markets; in some cases, flash loan attacks have been used to destabilize the price of a particular cryptocurrency. Flash loan attacks have also reportedly "stolen" funds from lending platforms. In recent research by Certik, flash loan attacks remain a significant pain point for web3 projects, with a total of $308,002,694 lost across 27 attacks in Q1 & Q2, 2022. For this reason, DeFi, crypto, and Web 3 users need to be aware of the risks associated with flash loan attacks and how to prevent such attacks.
In this blog post, we glance at the flash loan attacks and how they have affected DeFi space due to the negligence of risks associated with them. Then we discuss the top flash loan attacks of 2022 and a few techniques for enhancing security in the DeFi ecosystem.
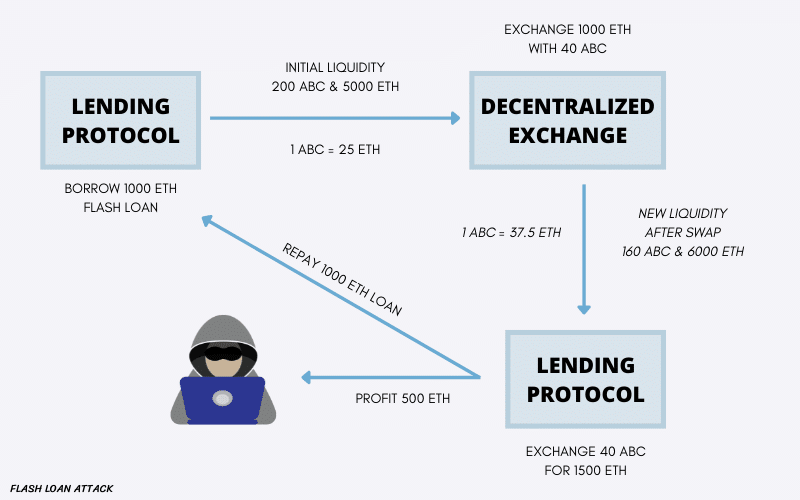
What Is A Flash Loan Attack?
A flash loan attack exploits a flaw in smart contract code to allow someone to borrow money without collateral. Hackers can use this attack to steal money from exchanges or manipulate the prices of tokens. Flash loan attacks are possible because of the way that smart contracts are programmed. Smart contracts are written in codes that are executed on a blockchain. Attackers can exploit these codes to find vulnerabilities that allow them to borrow money and use it to buy assets before selling them off and repaying the loan.
How Do Flash Loan Attacks Work?
Flash loan attacks are possible, as the decentralized lending platforms allow users to borrow money without collateral, and they set the interest rate based on the risk of the loan. This makes it attractive to hackers, who can use the loans to exploit price differences on different exchanges.
A hacker borrows money from a lending platform without collateral and uses it to attack another target. This is done by transferring the loaned money to a wallet controlled by the hacker, then using that money to buy up a large amount of the target asset on a decentralized exchange. The price of the target asset is then driven down, and the hacker can sell their holdings for a profit.
Source: Cryptotimes.io
Top 5 Flash Loan Attacks In 2022
Beanstalk Farms
Beanstalk is a decentralized credit-based protocol that issues stablecoins without collateral and instead relies on a decentralized credit system.
Total Loss: $182,284,430
The project's protocol governance system was attacked by obtaining the project voting rights, allowing the attacker to carry out an urgent execution of a malicious proposal stealing project cash. PeckShield claims that the hacker has already transferred the entire $80 million to the cryptocurrency asset mixer provider Tornado Cash to cover their tracks. Additionally, the offender gave Ukraine $250,000 worth of USDC stablecoin.
Fei Protocol
Fei Protocol is an Ethereum-based algorithmic stablecoin protocol that manages its stablecoin, pegged to the US dollar, using the Protocol Controlled Value (PCV) approach.
Total loss: $79,348,386
This attack primarily took advantage of the reentrancy flaw in the cEther implementation contract used by Rari Capital. The project's fundamental protocol was vulnerable, and the attacker targeted multiple smart contracts. The attacker begins with a balance flash loan. Utilize the proceeds from a flash loan to fund mortgage lending at Rari Capital while maintaining the terms of the company's cEther implementation contract. The attacker then calls back the attack function created in the attack contract to withdraw all of the tokens in the pool affected by the protocol.
Deus Finance 2
DEUS Finance is a marketplace for decentralized financial services, where the DEUS DAO provides the infrastructure necessary for third parties to create financial instruments. Platforms for trading synthetic stocks, options, and futures.
Total loss: $ 15,700,000
With the aid of the flash loan, Deus' attackers were able to temporally manipulate the DEI token price and utilize it to borrow money from the liquidity pool, which included the USD coin (USDC) stablecoin and DEI. The attacker was able to borrow money, fraudulently increase the value of particular assets, and profit after paying back the loan.
Elephant Money
Elephant money is the DeFi protocol for economic inclusion and helps its community accumulate wealth through active and passive cash flows.
Total loss: $11,340,000
The Elephant money attack was a classic case of price manipulation, in which the attackers sold thousands of ELEPHANT tokens for borrowed Binance Coin wrapped in a flash loan. According to reports, the attackers created TRUNK stablecoins, which increased the value of ELEPHANT tokens, before exchanging both coins for Binance's US Dollar stablecoin and Binance Coin. The attacker got around $4 million in profit in one attack round and used the same method to steal more money.
Saddle
The Saddle is a decentralized automated market maker built on Ethereum Blockchain tailored for pegged value crypto assets like wrapped BTC and stablecoins. In addition to assisting DeFi teams in bringing pegged asset swaps to any blockchain or L2 network, Saddle intends to develop as a DeFi lego block.
Total loss: $10,984,288S
The main reason for the attack was a breach used to carry out Multiple transactions on the wallet, and the attacker exploited sUSD; susd is a synthetic USD token by the Synthetix protocol that keeps track of the US dollar (US$) price through the price feeds. $2.9 million USDC was swapped for sUSD. With the help of the white hat hackers, Saddle finance could retrieve around $3.8 million of the stolen fund.
How To Prevent Flash Loan Attacks
There is no answer on concrete solutions to prevent the rising amount of flash loan attacks. But DeFi developers can take significant actions to address this problem.
Use Of Decentralized Oracle
The safest option is using decentralized oracles, limiting the attack vector for flash loans that employ many sources to establish the "actual price." To ensure the accuracy of their information, some decentralized oracles go a step farther and save real price data on the blockchain to assure the correctness of data so that flash loans can avoid manipulating prices.
Smart Contract Audit
The bug in the smart contract code is one of the main reasons exploiters may get away with flash loan assaults. DeFi projects can remedy their protocol's flaws and weaknesses by having it audited. The vulnerability management solution from BlockChainSentry can help DeFi projects implement an end-to-end security strategy in the struggle to safeguard your smart contracts. Our blockchain security solutions can help identify smart contract exploits and other flaws and helps project developers respond quickly and neutralize threats.
Flash loan attacks are among the most frequent types of attacks the DeFi platform sees, and they are likely to stick around for some time. These assaults are regarded as the least expensive and easy to pull off by hackers. Since flash loan attacks have become far more profitable and more frequent, the only way developers can survive is to build a concrete security posture. If they don't try to improve their security measures, we will never stop hearing about these attacks every week, which result in significant losses.